The systolic blood pressure, or SBP, is the measurement of the pressure in the arteries taken whenever the heart beats, whereas the diastolic blood pressure, or DBP, is the measurement taken whenever the heart is at rest in between beats. For example, if the systolic blood pressure is 100 and the diastolic blood pressure is 80, the blood pressure would be expressed as "100/ 80mmHg."
Definition of low blood pressure?
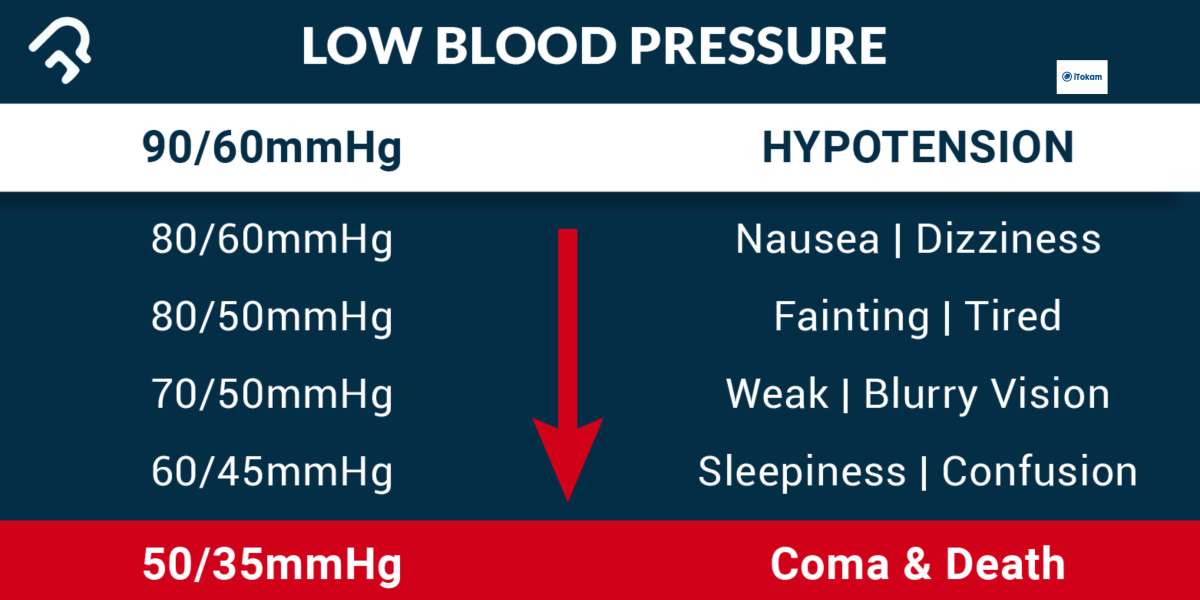
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension is a decrease in systemic blood pressure. It could be defined also as a measurement of less than 90/60 mm Hg for blood pressure. People are said to have normal blood pressure if their systolic blood pressure is between 90- and 120-mm Hg and their diastolic blood pressure is between 60- and 80-mm Hg. In other words, normal blood pressure ranges from 90 to 120 mm Hg and 60 to 80 mm Hg, however high blood pressure is defined as a BP reading that is higher than 120 mm Hg or 80 mm Hg.
Hypotension is a relatively benign condition that is under-recognized mainly because it is typically asymptomatic. It only becomes a concern once pumping pressure is not sufficient to perfuse key organs with oxygenated blood. This leads to symptoms impacting the quality of life of a patient.
Symptoms of Hypotension
Since low back pain rarely results in any symptoms, it is possible that the condition does not require treatment. The blood pressure of these individuals is consistently low, which is typical for them. When there is an abrupt drop in blood pressure, however, or when it is caused by a health concern, hypertension can be treated.
In patients who exhibit these symptoms, it may be an indication that blood supply to the heart, brain, and other essential organs is inadequate, which can lead to a cardiovascular event such as a heart attack or stroke.
- Dizziness and fainting can be brought on by a quick decrease of just 20 mmHg, for example, a sudden drop from 100 mmHg SBP to 80 mmHg SBP. Larger dips in blood pressure, such as those caused by uncontrolled hemorrhage, severe infections, or allergic reactions, can be fatal.
- Dizziness, also known as lightheadedness,
- blurred vision,
- malaise (a general sensation of illness or discomfort),
- confusion,
- headache,
- fainting,
- neck or back pain,
- heart palpitations, and a general feeling of weakness are some of the frequent symptoms of low back pain (LBP).
Causes of Hypotension (LBP)
Problems with the autonomic nervous system have been linked to hypotension (LBP). Because it delivers "fight-or-flight" signals to the heart and other body systems, the autonomic nervous system (ANS), like many other body systems, is able to regulate blood pressure. These signals, depending on the circumstances, can either increase or reduce blood pressure.
Other causes include blood loss as a result of an injury, which can result in a fast drop in blood pressure;
- dehydration, which reduces blood volume
- pregnancy
- diabetes
- Emotional stress, fear, insecurity or pain (the most common causes of fainting)
- Internal bleeding, such as perforated ulcer
- cardiac disorders such as arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats); and medications used to treat hypertension, Parkinson's disease, or depression.
Also Read: 7 Sexual Benefits Of Cloves To Women.
Types of low blood pressure
Orthostatic hypotension (also known as postural hypotension): is an abrupt drop in blood pressure that occurs when a person rises up from a seated or lying down position. This could be the result of things like dehydration, pregnancy, being in bed for an extended period of time, certain drugs, or certain medical conditions. It is often more prevalent in those of senior age.
- Postprandial hypotension: is a drop in blood pressure that happens one to two hours after eating. It is most common in elderly people who have hypertension or ANS illnesses like Parkinson's disease. It is recommended that persons in this situation eat only moderate amounts, abstain from alcohol, and consume a lot of water.
- Neurologically mediated Hypotension: is something that often happens when children and young people have stood for extended periods of time. It's possible that the heart and the brain aren't properly communicating with one another.
- Shy-Drager syndrome (Multiple system atrophy with orthostatic hypotension.) It is an extremely uncommon condition that affects the neurological system, which is responsible for automatic functions such as digestion, respiration, blood pressure, and heart rate. It is characterized by having extremely high blood pressure when the patient is lying down.
Treatment of low blood pressure
This is dependent on the underlying reason that has been diagnosed, however the majority of cases of LBP are normal and do not require treatment. When treatment is necessary, however, it may consist of alterations to the patient's way of life, medical treatment, or a mix of the two.
The following are some modifications in lifestyle that can help manage LBP:
Dos
Proceed with caution as you rise from a seat to a standing position.
When getting out of bed, move carefully from a laying position to a sitting position and then to a standing position.
Eat small, frequent meals. It's possible that lying down or sitting still for a bit after you eat is very necessary.
Drink more water.

Don’ts
Standing for extended periods of time should be avoided.
Avoid making rapid changes to your posture, such as bending down or standing up.
Avoid caffeinated drinks at night.
Try to limit the amount of alcohol that you consume.
If the underlying reason can be identified, medical treatment may be administered to alleviate the symptoms. However, the majority of cases of low blood pressure can be cured without the need of hypertensive medication if the patient simply makes some lifestyle adjustments or receives treatment for the underlying reason.
A blood transfusion, on the other hand, may be required to save the life of someone who is hemorrhaging continuously or who has experienced a sudden loss of blood that is greater than 20 mmHg.
In conclusion, Medication and sometimes even more immediate management may be necessary for those whose low blood pressure causes symptoms or is the consequence of a sudden drop in blood pressure that is greater than 20 mm Hg. However, in the majority of people, LBP is normal and it does not attract any special attention to our health.